History
Alois Alzheimer

Alois Alzheimer Biography
Aloysius Alois Alzheimer, better known as Alois Alzheimer was a German neurologist and psychiatrist, recognized for being the first to identify the symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease. He was born in Marktbreit, Germany on June 14, 1864, and was the son of Eduard Alzheimer and Barbara Theresia Busch. Since he was a child he was interested in everything related to science.
He completed his medical studies at the universities of Tübingen, Berlin, and Würzburg, so in 1887 he graduated as a doctor. A year later, he began work as a resident doctor in the hospital for the mentally ill and epileptic in Frankfurt, where he remained for 7 years and was promoted to the chief doctor. At that time, Alzheimer studied psychiatry and neuropathology. He also met the neurologist Franz Nissl, with whom he made several investigations on the pathology of the nervous system. This work gave rise to the six volumes of histological and histopathological studies of the cerebral cortex, published between 1906 and 1918.
For the month of April of the year 1894, he married Cecilia Alzheimer Geisenheimer, with whom he had 3 children.
In the year 1901, Alzheimer met Auguste Deter, a 51-year-old woman with strange behaviors and increased short-term memory loss. The patient became an obsession for Alzheimer, and he started doing many studies during the following years.
In search of a place to combine research with clinical practice, Alois Alzheimer became Emil Kraepelin’s research assistant at the Munich School of Medicine, where he led a new laboratory for brain research. At that time, he published several articles related to brain conditions and diseases.
For the year 1906, after several analyzes and studies in the patient, Alzheimer identified an uncommon disease of the cerebral cortex, which caused loss of memory, disorientation, and hallucinations to finally reach death. This was what had caused Auguste Deter’s death.
In the year 1907, he was at the psychiatric convention of Tubingen, where he explained the case of who had been his patient, emphasizing that of the post-death analysis of the brain, which showed a shortage of cells in the cerebral cortex and groups of filaments located between nerve cells.”
Finally, in the year 1910 Emil Kraepelin, published his treatise “Psychiatry” where he defined the new form of dementia discovered by Alois Alzheimer, calling it “Alzheimer’s disease.”
For the year 1912, King William II of Prussia hired him to work at the University of Breslau, naming him professor of psychiatry and director of the Neurological and Psychiatric Institute.
He was co-founder and co-publisher of the journal “Zeitschrift für die Gesamte Neurologie und Psychiatrie.” In his career, he did not write works by himself, he always chose to work in a group.
Alois Alzheimer died on December 18, 1915, in Wroclaw at the age of 51 years, because of an infection that he acquired from streptococcus during a train trip, which generated fever, kidney failure, and strong flu.

History
Robert Oppenheimer
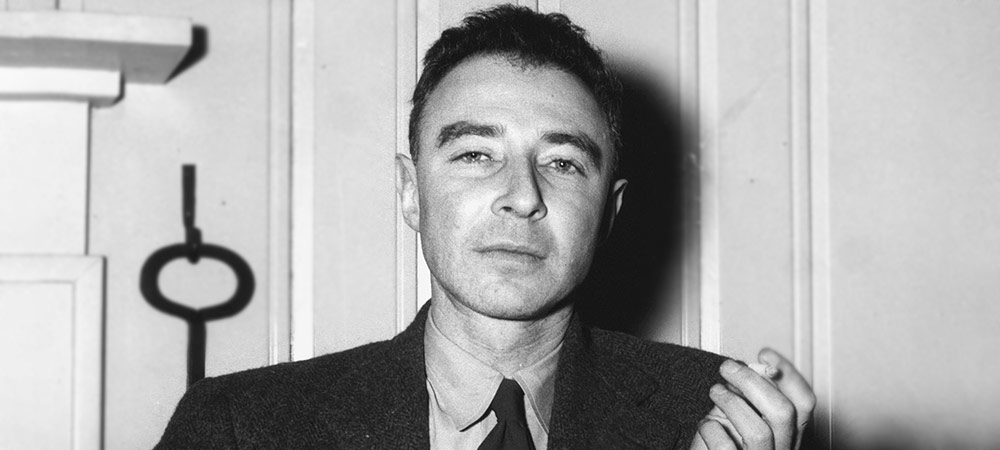

Robert Oppenheimer Biography
Julius Robert Oppenheimer (April 22, 1904 – February 18, 1967) was a physicist widely acknowledged as the father of atomic bomb. He was born in New York City, United States. Oppenheimer is renowned for his pivotal role in the development of the Manhattan Project during World War II, which culminated in the creation of the first atomic bombs.
Early years
Robert Oppenheimer was an American theoretical physicist, scientist, and university professor. He was the son of German-born Julius S. Oppenheimer and artist Ella Friedman. Coming from a wealthy and educated family in New York, his father was a Jewish owner of a significant fortune amassed through his textile factory. This allowed Oppenheimer to enjoy certain comforts and attend the best schools in the city.
In this regard, he was educated at the Ethical Culture School in New York, where he excelled as the top student, with some teachers even asserting that he was better than many of them. Upon graduating from school, he enrolled at Harvard University, where he stood out in all areas, from chemistry to Eastern philosophy, Greek, and Latin, completing his studies at the age of 21.
Career
After some time, Robert Oppenheimer decided to delve into the world of physics, capitalizing on both his aptitude for the subject and its burgeoning prominence across Europe. He moved to England, where he worked with Ernest Rutherford and J. J. Thomson. Alongside these two great scientists, he felt somewhat inadequate, as he believed his performance did not meet the required standards. However, Oppenheimer did not give up.
With the passage of time, he learned from his mentors, and by 1925, feeling more adapted, he began researching atomic energy and secondary-atomic particle energy processes at the Cavendish Laboratory.
A year later, he was at the University of Göttingen, collaborating with Max Born to develop his classical contribution to molecular quantum theory, known in physics as the “Born-Oppenheimer method”. He returned to his home country to teach theoretical physics at the California Institute of Technology and the University of Berkeley between 1929 and 1942. Oppenheimer was a highly political person. Therefore, in the 1930s, he decided to align himself with communist students to support the Republic during the Spanish Civil War, but certain actions led to the demise of his sympathy for the Communist Party.
Contribution to the Manhattan Project

General Leslie Groves alongside Oppenheimer in the development of the Manhattan Project (Circa 1944)
The civil and political situation in Europe was becoming increasingly dangerous. By 1939, Albert Einstein and Leo Szilard warned the U.S. government about the dangers of nuclear energy falling into the hands of the Nazis. In response, President Franklin Roosevelt initiated the project for creating the atomic bomb, which was initially under military control, led by General Leslie Groves, an engineer known for overseeing construction projects, including the Pentagon. Later, Oppenheimer was brought on board to manage the administration of the project, which culminated in the construction of the atomic bomb by 1945.
Oppenheimer’s most significant contribution to the Manhattan Project was his leadership and effective coordination among diverse teams of scientists. His vision and problem-solving skills were crucial in overcoming the scientific and technological challenges involved in building an atomic bomb. He supervised the design and testing of the first atomic bombs, including the successful detonation of the plutonium bomb at the Trinity test site in New Mexico on July 16, 1945.
This American physicist had the support of many prominent figures in science, such as the great scientist Werner Heisenberg, Erwin Schrödinger, Max Born, Wolfgang Pauli, Paul Dirac, and Enrico Fermi, with whom he also developed close friendships. The work carried out by these scientists on quantum physics provided significant support for his own research. He gained valuable insights into quantum and relativistic physics, which kept him abreast of new scientific developments. He made contributions to the application of quantum theory to the concept of electron spin.
In his role as the director of the Institute for Advanced Study in Princeton, he fostered discussion and research in quantum and relativistic physics. In 1953, his past ties with the Communist Party led to certain defamation issues. As a result, he was called to a security hearing where the accusation was dismissed, but his access to military secrets was still prohibited. One of the institutions that attacked the scientist the most was the Federation of American Scientists. Oppenheimer was humiliated, and his communications were monitored. Nine years later, President John F. Kennedy, in an effort to rectify this mistake, awarded him the Enrico Fermi Award, granted by the Atomic Energy Commission, which he received from President Johnson himself.
“Now I Am Become Death, the Destroyer of Worlds”.
Oppenheimer, confessed to President Harry Truman, that he was not entirely comfortable with the fate of the atomic bomb. After some time, the Cold War erupted, and the Soviet Union announced its possession of an atomic weapon. In response, the United States decided to develop an even more powerful weapon. They approached Oppenheimer to lead the Atomic Energy Commission, but he declined the offer, resulting in his removal from the position. However, he remained the director at the Institute for Advanced Study, thanks to the support given by Einstein, Von Neumann, and Bohr.
After this event, his life took a different turn as he decided to distance himself from the laboratories and leaned towards writing about the studies conducted throughout his scientific career. Notable works include “Science and the Common Understanding” (1954) and a book related to electrodynamics (published posthumously in 1970). In the aftermath of the events in Japan and the grave consequences the atomic bomb had on humanity, he made several proposals aimed at internationally regulating the use of atomic energy to ensure peace.
He staunchly opposed the creation of the hydrogen bomb. However, despite his efforts and those of the General Advisory Committee of the Atomic Energy Commission, its development continued. Disheartened, Oppenheimer made the decision to retire from Princeton in 1966. A year later, on February 18, 1967, he passed away from throat cancer.
Filmography
Visual works inspired by Robert Oppenheimer:
- “Fat Man and Little Boy” (1989): Oppenheimer was portrayed by Dwight Schultz in this film.
- “One Day” (1989): The scientist was portrayed by David Strathairn.
- “Oppenheimer” (2023): The biography of Julius Robert Oppenheimer was brought to the screen in this movie, based on the biographical work “American Prometheus” by author Kai Bird. The character of Julius Robert Oppenheimer was played by Cillian Murphy and directed by Christopher Nolan.
History
Threads

History of Threads
Threads (July 5, 2023) is an application and social media developed by the Meta group, designed to compete with Twitter. While it shares some features with Twitter, it has its own distinctive approach. This application has been specifically designed to share text-based updates and engage in interactive public conversations.
What is Threads?
Threads is a new application and social network created by the Instagram team, which is part of the Meta group, led by billionaire entrepreneur Mark Zuckerberg. The launch of Threads has had a positive impact on the market, as Meta’s stocks experienced an increase of nearly 3% during an unfavorable session on Wall Street. Furthermore, in after-hours trading, the stocks continued to rise, increasing by almost 1%. This indicates a favorable reception from investors and the market.
The application has been specifically designed to share moments through text-based updates. It provides a unique and standalone space for real-time posting and engaging in public conversations. With the new application, you have the opportunity to follow and connect with friends and creators who share your same or similar interests, including the people you follow on Instagram.
Threads has been developed with the aim of competing with Twitter and presents features and similarities that go beyond simple text sharing. Just like on Twitter, in this new app, users can create threads, share photos, videos, and links. The application is currently available for launch on iOS and Android devices. It is worth noting that currently, an Instagram account is required to access the app.
Mark Zuckerberg and his Meta team have taken advantage of the recent changes in Twitter following the acquisition by Elon Musk. Twitter has reduced some of its security options, reserving them exclusively for users who purchase Twitter Blue. Meta has identified this gap and has seized the opportunity to attract users to join Threads. The new application stands out for maintaining a wide variety of security controls and providing a safe experience for users.
“The idea is to build an open and friendly space for communities”- Adam Mosseri.
Differences between Threads and Twitter
- Threads currently follows the same security policies as Instagram.
- In Threads, it is not possible to save posts as drafts. You must share posts immediately or delete them.
- Threads does not have a set limit on the number of posts that can be viewed. There is no maximum limit on viewed posts in Threads, unlike the recent limitation imposed by Twitter of 600 posts.
- The new social media does not yet have direct messaging, unlike Twitter.
How to create an account on Threads?
To get started, you need to go to the mobile device’s app store and search for “Instagram Threads”. Once found, click on download and install the application. Once installed, open the app and access Threads using your Instagram username.
Next, complete your personal information and adjust the security options according to your preferences. Once this process is done, you will be ready to explore the application, change your profile picture, and start following people and topics that interest you.
It should be noted that automatically, anyone under the age of 16, or under the age of 18 in certain countries, their profile will be set to private when joining Threads.
When Instagram users sign up for this new social network, they receive a Threads badge on their Instagram profile. This badge displays a number indicating the sequence in which they created their account on this new app.
How is Threads used?
Threads offers a user interface similar to that of Twitter, allowing users to interact with other users’ posts from the “Home” section. Additionally, through the search icon, it is possible to find other users on this red social.
In the “Home” section, you will find posts from the people you follow, as well as recommended content from new creators that you have yet to discover. Posts have a limit of 500 characters and can include links, photos, and videos up to five minutes in length. Additionally, you have the option to easily share a Threads post to your Instagram Story or share it as a link on the platform of your choice.
To create a thread in this app, simply click on the notebook icon. Once you have written your message, publish it and continue with the text at the bottom. Just like on Instagram, the heart icon shows recent activity on your account, allowing you to see feedback and interaction with your posts.
Similarly, it is important to note that if you block an account on Threads, the same account will also be blocked on Instagram. This means that blocking actions are applied collectively on both platforms.
How to delete an account on Threads?
It is important for users to note that if they wish to delete their account on Threads, it is likely that their Instagram account will also be deleted. Currently, the only available option is to temporarily deactivate the account on this application, but it can only be permanently deleted if you delete your Instagram account.
Artist
Metallica history
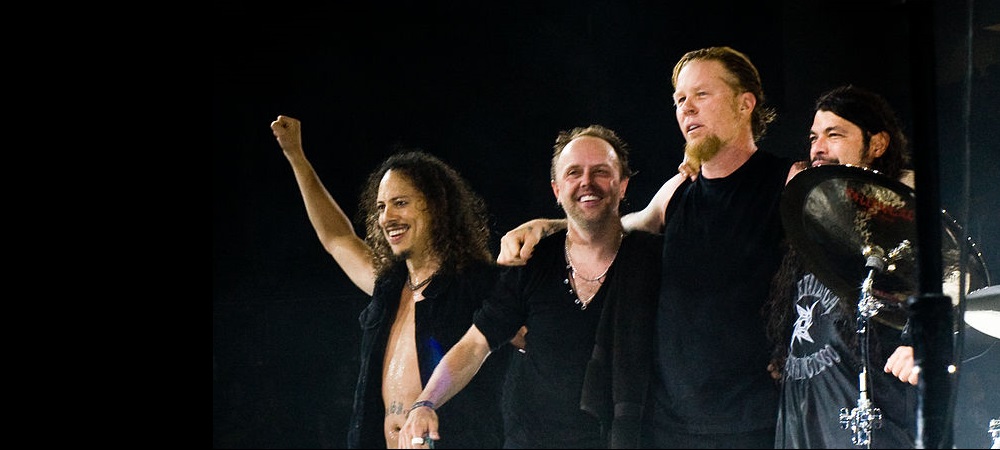

Metallica history
Metallica is an American thrash metal band from Los Angeles and based in San Francisco. It is considered one of the leading groups in the subgenre and throughout its 35-year career it has won numerous awards, including 9 Grammys, 2 American Music Awards, 2 MTV awards, 2 Billboard awards, and a star on the Hollywood Walk of Fame.
1980 – Beginnings
The history of the band begins in 1980 when Lars Ulrich, the son of tennis player Torben Ulrich, placed an ad in the magazine Recycler looking for a guitarist for a metal band influenced by the British New Wave of Heavy Metal. James Hetfield responded to the ad and joined Ulrich as the first members of the band. Ron McGovney joined as bassist and Lloyd Grant as lead guitarist. With this first formation, the band recorded its first demo, Hit the Lights, considered one of the first thrash metal songs. However, they soon realized that the lineup was not working and Lloyd was replaced by Dave Mustaine.
Despite the early disastrous performances due to the lack of experience of the members, the band continued and released No Life ’till Leather, showing a more aggressive sound. Additionally, Ron McGovney was replaced by Cliff Burton as bassist and Dave Mustaine was replaced by Kirk Hammett due to his alcohol addiction. Since then, James Hetfield has taken on both the role of rhythm guitarist and singer.
1983 – Release of ‘Kill ‘Em All’
With this new lineup and having Johnny Zazula as their manager, the band released in 1983 Kill ‘Em All, which gained notoriety in the metal scene and sold more than 300,000 copies. After a tour of the United States and a concert in Holland where they reached their largest audience to date, with 5,000 people, the band released the album Ride the Lightening with Megaforce Records in 1984, which received critical acclaim for its melodic sound.
“1991 – Release of the ‘The Black Album'”
After this work, the band released Master of Puppets in 1986 and embarked on a promotional tour that was cut short by an accident in which the bassist Cliff Burton died. After reflecting on their future, the band incorporated Jason Newsted and recorded …And Justice for All, an album with a denser sound that, despite its commercial success and a Grammy nomination, received criticism for being unoriginal and moving away from heavy metal. However, it wouldn’t be until the release of their album Metallica in 1991, known as The Black Album, that they reached great success, selling half a million copies in the first week of sales in the United States and reaching the top of the Billboard chart. This work led to two similar albums, Load in 1996 and ReLoad in 1997, which received negative reviews for their proximity to alternative rock and their distance from traditional heavy metal, disappointing their older fanbase.
“2001 – Documentary, Tours, Awards”
In 2001, Jason Newsted left the band and Metallica struggled to find a suitable replacement for some time. Therefore, they had to record their next album, St. Anger, with their producer Bob Rock playing bass. However, Robert Trujillo soon joined the band’s lineup. Three years later, the documentary Some Kind of Monster was released, which portrays the recording process of the last album and the internal conflicts that the band had with Dave Mustaine. After a tour in 2006 in which they played Master of Puppets again to celebrate its 20th anniversary, and the release of a compilation of their videos titled The Videos, Metallica was inducted into the Rock and Roll Hall of Fame. Later, they released Death Magnetic in 2008 and the conceptual album Lulu in 2011, which was poorly received by their fans. In 2012, the band founded their own record label, Blackened, and performed a concert in Antarctica to raise awareness about polar melting and environmental crisis. In 2016, they released Hardwired… to Self-Destruct. Currently, the band is still active.
Culture
Cleopatra
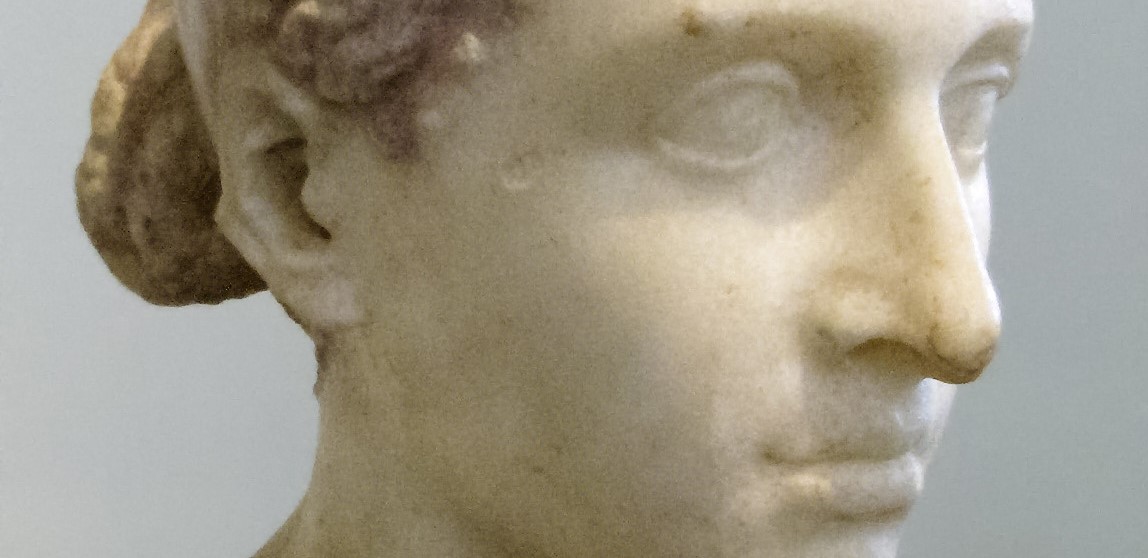

Biography of Cleopatra
Cleopatra (69 BC – August 12, 30 BC) was the last Queen of Egypt, belonging to the Ptolemaic dynasty. She was born in Alexandria, Egypt. Her father was Ptolemy XII and her mother was Cleopatra V Tryphena. Cleopatra married her brother Ptolemy XIII, as a strategy to maintain the reign, then they both inherited the throne in 51 BC. Cleopatra is said to have possessed exceptional beauty. Her father was not well-liked by his people as he showed little interest in the problems of the Egyptian people, He was a corrupt ruler who squandered the kingdom’s money on lavish parties.
She was able to maintain her throne thanks to the Roman help she received in exchange for her continuous bribes and promises of various tributes. The Romans supported the king because he promised them easy access to the gold and wealth of Egypt. In each conflict, Rome played the role of arbitrator in the popular uprising, Ptolemy, went to Rome in search of military aid to suppress it. His wife Cleopatra and one of her daughters were left as regents of the country, then his wife died. The Alexandrians placed Queen Berenice IV on the throne and sent a delegation to Rome to arbitrate the conflict between father and daughter.
Soon after, Ptolemy XII was able to defeat the army of Archelaus, second husband of Berenice IV, and was returned to the throne. To ensure power, he had his daughter Berenice executed, it was the year 55 BC. The king died four years later, leaving the throne to his daughter Cleopatra VII Philopator and his son Ptolemy XIII Dionysus II. Cleopatra was the first of this dynasty to learn to speak the Egyptian language; she also learned Greek, Hebrew, Syrian and Aramaic and possibly Latin. She was also educated in literature, music, political science, mathematics, astronomy and medicine.
The situation in Egypt was becoming worse, farmers suffered severe famines, the Egyptian currency was weakening and the slow bureaucracy was hindering recovery: the country was becoming increasingly dependent on Rome. In response, farmers staged uprisings and created bands of outlaws that caused great harm; Additionally, the royal family also did not have good relations. Her younger sister Arsinoe, disagreed with her policy of helping the Romans and wanted to reach the throne. Ptolemy XIII, very young and manipulable, was practically handled by three advisors who forced him to expel his sister from the throne by overthrowing her with a command led by his advisors Potino and Aquilas.
Cleopatra attempted to regain power, gathering a good army for this purpose, although she did not succeed. Soon conflicts broke out between the two brothers and spouses, which led to the overthrow of Cleopatra. However, when the Roman civil wars began: Julius Caesar went to Egypt and helped Cleopatra in the conflict with her brother. During the Alexandrian War, both Pompey and Ptolemy XIII died, and the legendary Alexandria Library was burned.
Cleopatra was first and foremost a solution for Julius Caesar, and also his lover, she tried to use her influence over Caesar to restore Egypt’s hegemony in the Eastern Mediterranean as an ally of Rome; the situation intensified when she had a son with Julius Caesar: Caesarion. When Julius Caesar was assassinated in 44 BC, Cleopatra attempted to seduce his immediate successor: consul Mark Antony. Being allies, they imposed their force in the East, creating a new Hellenistic kingdom that managed to conquer Armenia in 34.
Cleopatra, in addition to being a skilled ruler, was also known for her beauty and intelligence. She was fluent in several languages, including Egyptian, Greek, Hebrew, Syrian, and Aramaic, and was well-educated in literature, music, politics, mathematics, astronomy, and medicine. She used her charm and wit to strategically seduce powerful men in order to maintain control of her kingdom. She had a son, Cesarian, with Julius Caesar and later became the lover of Mark Antony. However, after the defeat of their alliance and the death of Antony, she was captured by Augustus and brought to Rome as a war trophy.
In the face of this situation, Cleopatra had herself bitten by an asp to end her life. Augustus took advantage of the situation to also murder her son Cesarión, thus extinguishing the Ptolemaic dynasty and later annexing Egypt to the Roman Empire. Cleopatra’s life inspired many writers, painters, sculptors and filmmakers. For example, between 1540 and 1905, over 200 plays, five operas and five ballets emerged. Let’s mention some important literary works: Cleopatra and Mark Antony (1606) by William Shakespeare, All for Love (1678) by the Englishman John Dryden and Caesar and Cleopatra (1901) by George Bernard Shaw. Even one of the comics of the popular Asterix the Gaul was dedicated to her.
Cleopatra has been the subject of many paintings and sculptures. Additionally, her life has been depicted in films, such as Cléopâtre (1899) and the famous and controversial 1963 production directed by Joseph L. Mankiewicz: Cleopatra, starring Elizabeth Taylor. Another production, Marco Antonio y Cleopatra was released in 1972. A more recent, less ambitious film was Cleopatra (1999). Later, the British Museum dedicated an exhibition to Cleopatra, sparking an interesting debate about her beauty.
History
Grupo Firme
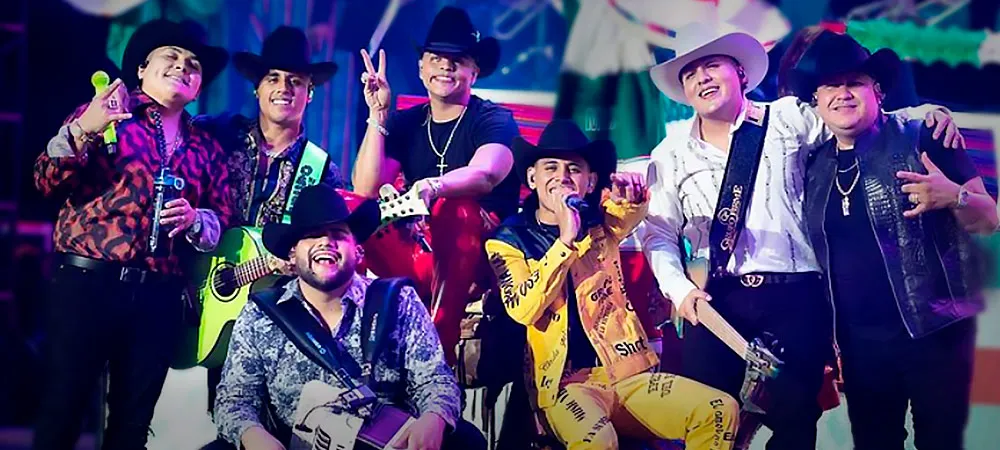

History of Grupo Firme
Grupo Firme is a musical group of Mexican regional music from Tijuana. It was created in 2014 and its members are: Eduin Cazares (leader and vocalist); Joaquín Ruiz (bass guitar); Jhonny Caz (vocalist), Abraham Hernández (second voice); Christian Téllez (bass); Dylan Camacho (accordion); and Fito Rubio (drums). Initially they made themselves known on social networks with some covers and in 2017 they made their debut with their first album Past, Present, Future. In 2018, their first hits, Pídeme, El Roto and Juro Por Dios came out and a year later they became famous with the hit El Amor No Fue Pa’ Mi, among other hits. Currently they are seen as the new fashionable group.
The beginnings
United by their love of music and coming from different parts of Mexico, the seven members of the group met in Tijuana. They grew up and began their careers in this city as members of different groups, although they knew each other from their work in the artistic industry. The founders of the group were Eduin and Joaquín, who coincidentally joined various groups before founding the group in early 2013 or 2014.
Joaquín and Eduin started in the group Reto Sierreño, then moved on to the groups Aventado2 de Tijuana and Los 4 de la frontera, and finally coincidentally joined the group Fuerza Oculta. This last group became, after some changes, the Grupo Firme, although it was initially called Grupo Fuerza. Because many groups had the same name, the members decided to opt for a synonym and chose “Firme”.
This is how Grupo Firme was born, with Eduin as the vocalist and leader, Joaquín on the bass guitar, Abraham and Jhonny as second voice, Christian on the bass, Dylan on the accordion, and Fito on the drums.
With the help of their manager and representative Isael Gutiérrez, who is also the head of the Music VIP Entertainment label, the group took its first steps in bars and events. At the same time, they made themselves known on social networks and other platforms by uploading covers of recognized artists, such as Los Tigres del Norte, José Alfredo Jiménez, Los Tucanes de Tijuana, and others. Often, the group uploaded songs at the request of the public, so they didn’t take long to have their own fanbase.
Grupo Firme: debut and career
In April 2017, after three years of performances and covers on social media, the group released its debut album, “Past, Present, Future”. This album consisted of twelve songs, highlighting “De Sol a Sol”, “Metas Cumplidas”, “Perdóname”, and “El de los Huaraches”. Although the album was not very successful, it managed to make the group known. A few months later, the group returned with “El Barco” (2017), a fifteen-song album with the tracks “El Bueno de Tijuana”, “Dile”, “Gente de Verdad”, and “La Interezada”.
In addition, that year, the group collaborated with Los Buitres de Culiacán Sinaloa on the album “En Vivo Desde Tijuana los Buitrones y los Firmes” (2017). Success finally arrived in 2018 with the singles “Pídeme”, “El Roto”, and “Juro Por Dios”. That year, the group was quite active, releasing singles, collaborations, and making several appearances. They even went to Colombia, where they were well received and recorded their “En Vivo desde Medellín Colombia” (2018). The album, which included the tracks “El Teclas”, “El Peña”, and “El Flaquito”, was quite popular within and outside of Mexico.
The group finally achieved fame in 2019 thanks to the releases of “Me Cansé de Amarte” and the hit “El Amor No Fue Pa’ Mí” (ft. Banda Coloso). Later came the successful “El Muelas”, “En Realidad” with Banda Coloso, “Lujos y Secretos” with Quinto V Imperio, and “Porque Te Quiero” with Luis Alfonso Partida “El Yaki”. They also released that year the singles “Qué Me Vas A Dar Si Vuelvo”, “El Panal”, and “A Ti Te Conviene” with Calibre 50.
The successes continued in 2020. The group began the year by releasing the single “La Estoy Pasando Mal”, and later collaborating with Enigma Norteño on the song “Mi Pretexto de Borracho”. Later they appeared on the single “Yo Diría” by Uziel Payan and collaborated with Marca MP on “El Güero”. In March, “Acábame de Matar” was released and in April they premiered “Quiero Pistear” with Luis Ángel “El Flaco”.
Their second live album, “En Vivo Desde Anaheim, CA”, was released in July of this year, including their biggest hits: “Pídeme”, “Que Me Vas a Dar Si Vuelvo”, “El Roto”, “Descuide”, “Porque Te Quiero”, “El Amor No Fue Pa’ Mí”, among others.
In 2022, the news is released that the band, Grupo Firme, breaks the attendance record with more than 280,000 people in Mexico City’s Zócalo. In this way, this renowned band surpasses the record that belonged to Vicente Fernández, who had 217,000 people. Prior to these last two, Justin Bieber and Shakira had the record, with the attendance of 210,000 people present in the Zócalo.