Author
Denis Diderot
Denis Diderot Biography
Denis Diderot (October 5, 1713 – July 31, 1784) was a philosopher and writer. He was born in Langres, France. He was the oldest son of a well-to-do worker. In his hometown, he studied at a school run by the Jesuit Order. He received the preparation to succeed as a canon to his mother’s brother. When he finished his studies, he decided to move to Paris in 1734 to study at the University of Paris degree in arts. Then, he worked for almost a decade as a mathematics teacher, as well as, Latin, Greek and modern languages.
Diderot used to be part of the Parisian bohemian world. Which helped him to strengthen his knowledge and met many characters dedicated to letters and the arts. Simultaneously he published without signature his first important work, Philosophical Thoughts (1746), in which he exhibits his deistic philosophy. He also worked as editor of an English encyclopedia of Ephraim Chambers, in it he served as a translator from English into French. Thanks to the collaboration of Jean le Rond D’Alembert, he led to a new writing that included 35 volumes. It was called “Encyclopedia or reasoned dictionary of arts and crafts”. This work was made in collaboration with Voltaire and Montesquieu. The Encyclopedia took a treacherous tinge, making propaganda of weight against ecclesiastical authority, superstition, conservatism and semi-feudal order.
In 1759 some volumes were vetoed, eliminated and then their circulation was forbidden issued by the Conseil du Roi. Despite the restrictions, Denis did not leave his job and managed to recover the remaining volumes astonishingly and managed to replicate them in secret. Over the months, the volumes of the Encyclopedia had increased to 17. The second edition was made several years later in 1780. Of his works, we can also highlight “The religious” (1796), “The nephew of Rameau” (1761), translated into German by Goethe, “Jacques the fatalist” (1796), “Letters on the blind for the use of those who see” (1749) and “D’Alembert’s dream” (1830).
He wrote the Essay on Studies in Russia and the Plan of an official Russian University, at the request of his great friend and adviser Catherine The Great, Empress of Russia. Years later, Diderot would sell her more samples for her library, in order to solve his pressing financial needs. In 1729, the foundation of the newspaper Salones began, this one focused on spreading the critics of the art exhibitions that were held every year in Paris.
He fell madly in love with a seamstress named Antoinette Champion, to whom he soon proposed marriage. Soon after they were married, against the will of his father, who planned to confine him in a convent to avoid this union. Unfortunately, their marriage was unsuccessful, they had to face the death of the first three children in their early ages. The only who survived was their last daughter. Due to the problems between them, they decided to separate. Later, he initiated a loving relationship with Madeleine de Puisieux. Diderot onwards dedicated his life to sharing with several lovers, the latest was Sophie Volland.
Years after the publication of his work Philosophical Thoughts, in which he proclaimed his deistic tendency, he generated a condemnation of the Paris Parliament. But this situation did not stop him from being admired by many. The publisher Andre Le Breton, looked for him and asked him to be the director of the Encyclopedia, and would be supported by D’Alembert. For much of his life, Diderot devoted his efforts to make what he was, without hesitation, his most emblematic work of the Enlightenment, which contributed to the beginning of a new thought, breaking the mental structures of the moment.
The problems arising from the publication of his ideas did not stop. In 1749, was imprisoned for a month in Vincennes for the crime of intellectual debauchery, due to the disclosure of his letter to the blind for use by those who can see. The authorities claimed that it contained a skeptical tone of the text and abundant agnostic postulates. In jail, he received several visits from friends and important people, such as Rousseau. When he was released, he clandestinely recruited, with the help of Rousseau, subscribers to the Encyclopedia but the Royal Council found out about it and forbade the replication of the work. Although the intercession of Madame de Pompadour facilitated the revocation of the verdict.
The Vatican also added its voice to the sentence against Diderot and his works, ordering a new suspension; D’Alembert was intimidated and forced to leave the company, despite this the unconditional support of Guillaume-Chrétien de Malesherbes allowed the printing to continue privately. In 1764, Diderot got the publication of the last ten volumes of the text and abandoned the responsibilities being the publisher. He preferred to take new paths in literary life.
Then, he began a period of intense literary production. His Thoughts on the interpretation of natures embodied in various texts, where he proclaimed the superiority of experimental philosophy over Cartesian rationalism. Certainly, many of his works remained unpublished until he died, although they were analyzed by his friends. Some of those works are two philosophical novels: The religious and Jacques the fatalist, as well as the masterful dialogue “The nephew of Rameau”, translated by Goethe into German in 1805.
At his 70, after being fighting against a gastrointestinal condition, Diderot dies on July 31 of 1784 in Paris.

Author
Yukio Mishima
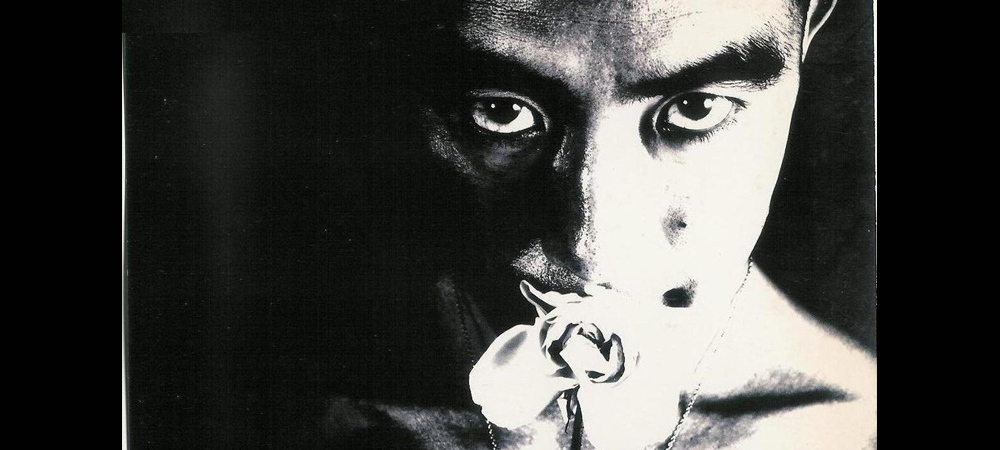

Yukio Mishima Biography
Yukio Mishima (January 14, 1925 – November 25, 1970) was a novelist, essayist, poet, and critic. He was born in Tokyo, Japan. His birth name was Kimitake Hiraoka. His father Shizue served as Secretary of Fisheries for the Ministry of Agriculture and his mother Azusa Hiraoka was completely devoted to the household. Despite this, Yukio was in the care of his grandmother, Natsu. During this time, the little boy had no contact with his parents. Natsu had mental problems and on many occasions, she was violent and had a madness crisis, this was later portrayed in Yukio’s works.
Beginnings
He learned a taste for letters and languages from his grandmother. When he was 12 years old, Mishima began to write his first stories, besides, he had already read a large number of books by authors such as Oscar Wilde and Rilke, as well as numerous Japanese classics. He attended a fairly prestigious school called the Peers School, attended by the Japanese aristocracy, and eventually extremely wealthy commoners. But, then he realized that it was the worst decision he made. He spent six miserable years in this place.
He never built friendships and was sometimes attacked by his peers. The only redeemable of that time was his participation in the editorial board in the literary society of the school, thanks to this he was able to achieve a great aptitude for literature. His performance was so good that he was commissioned to write a story for the prestigious literary magazine, Bungei-Bunka. He presented a work called Hanazakari no Mori (The forest in all its splendor). Later, the story was published in 1944, due to the war it had to be published in a small print run due to a shortage of paper.
In his youth, he suffered from tuberculosis, for this reason, he avoided doing military service and participating in the war. But for Mishima, it was taken as something negative and shameful. One of Mishima’s dreams before he became a writer was to be a kamikaze pilot. It was glorious for him to die heroically for his homeland. Frustrated, he decided to spend a lot of time writing until his father disagreed and forbade him. Mishima had to do it at night, supported and protected by his mother Shizue, who always read his stories. Then his father ordered him that he should study law and not literature.
Trajectory
Graduated from the University of Tokyo in 1947, Mishima never stopped writing during his university career. He got a job as a civil servant in the Japanese Ministry of Finance. But this work was so exhausting that he decided to leave it with the support of his father a year later.At that time he was able to dedicate all his time to writing. Mishima began to write all kinds of works: novels, plays, short stories, also poems, articles, and essays. Usually, his work was devoted to dark and stark themes, although contrasted with the delicacy and restraint of his style. His works led him to have worldwide recognition and to be the best-known Japanese writer abroad.
Mishima’s works
The way he expresses desire and rejection, beauty, and violence, is of great attraction to the public. Mishima received the influence of Nihon Romanha, a writer belonging to Japanese romanticism, who emphasized the unity of Japan and its cultural values. This was a vehicle to reinforce nationalist ideology and more in times of war. However, Mishima was also interested and was a great admirer of modern Western literature. His first extensive work The Forest in Flower, was published in 1941. This work, like The Cigarette (1946), and Thieves (1948) were written during World War II and show the total departure from the tragic reality of war and of defeat.
In 1949 he published a work that quickly gained popularity: Confessions of a mask, a work that marked the definitive consecration of him in the literary world. Although some critics showed bewilderment and reservations about the particularity of the subject (because the protagonist confessed his homosexuality) certainly this represented a novelty in Japanese literature. Mishima was drawn to the aesthetic values of Western classicism. The Golden Pavilion (1956) was his most successful work in the 1950s.
In 1958, he traveled to the United States and upon his return, Mishima married the daughter of a well-known painter. A year later, Kyoko’s House was published, it did not receive the favors of the critics. He always tried to reflect his taste for the values of the authentic Japanese based on the values of the samurai. In this sense, fascinated by the ideology of warriors, he wrote The Way of the Samurai and In Defense of Culture (1968). Mishima presented himself as a defender of the restoration of the values of the prewar and militaristic culture. The author was a man concerned about corporality and the state of the body, for this reason, he was a lover of the Martial Arts.
From 1955 Mishima began an intense program of physical activity and also resorted to military training at the Sietai base, together with a group of university students. His enormous literary production, among which, along with those already mentioned, stand out: The prohibited color (1951), The death of mid-summer (1953), The voice of the wave (1954), The taste of glory (1963) and Thirst for love (1964).
After the Banquet (1960), one of his most successful novels, he wrote Patriotism (1961) and Death in the afternoon, and other stories (1971), a compilation of short stories representative of a time when he was dying in the name of noble ideals.
Among his theatrical production of these years, it is worth mentioning Madame de Sade (1965) and My friend Hitler (1968). His most popular work is: The sea of fertility, composed of the novels Snow of spring (1966), Runaway horses (1968), The temple of the dawn (1970) and The corruption of an angel, completed the latter days before his death. In this work, a critique of Japanese society is made for the loss of traditional values. Yukio Mishima was concerned about the strong westernization of his country and analyzed its transformation from a pessimistic and critical perspective.
This terrible vision of Mishima led him to embrace suicide as the only way out of him, ending his life on November 25, 1970.
Author
Walter Scott
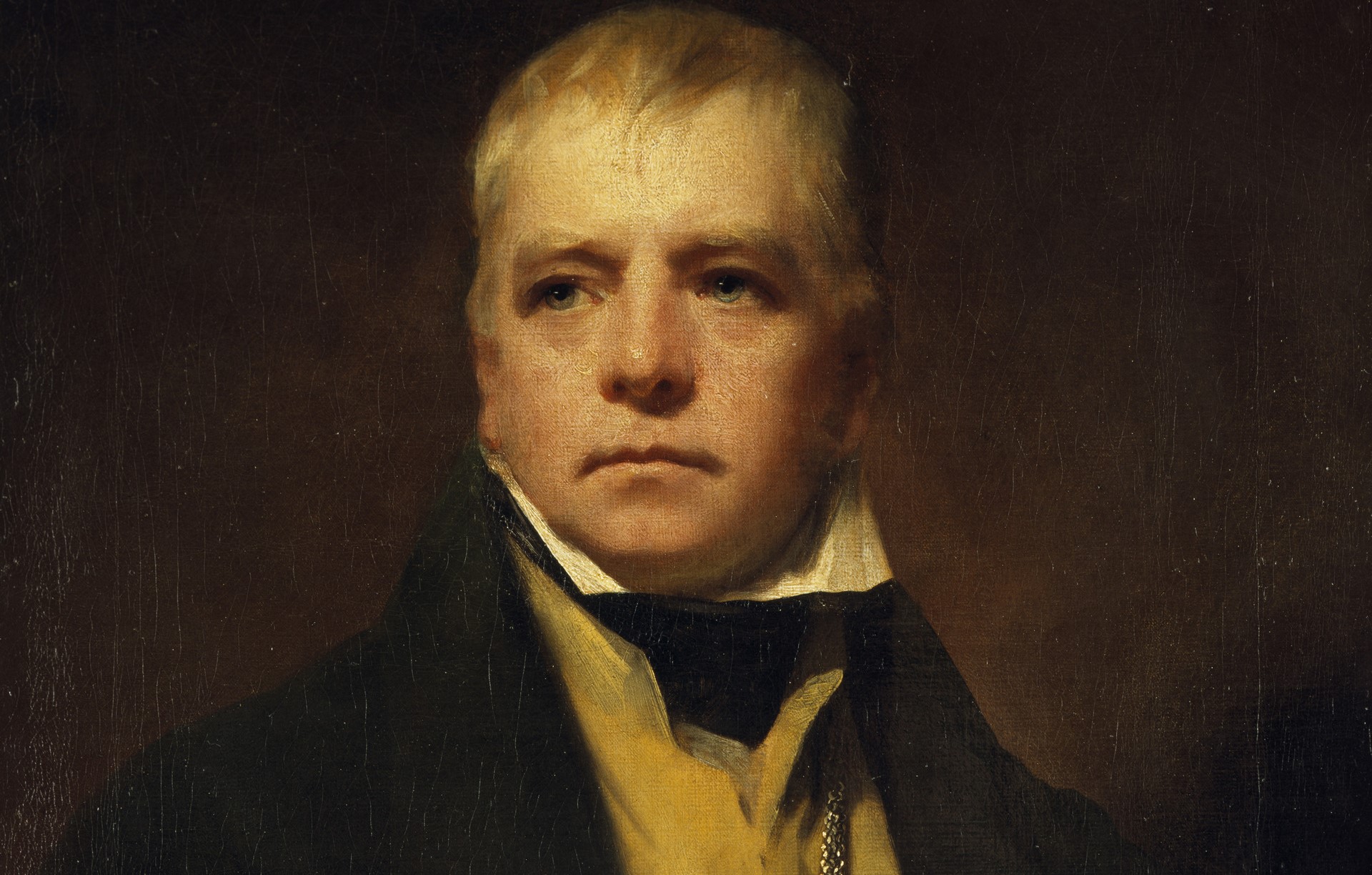

Walter Scott Biography
Sir. Walter Scott (August 15, 1771 – September 21, 1832) was born in Edinburgh, Scotland. British writer, poet, and lawyer considered the founder of the historical novel. Scott was one of the key figures of the Romantic Movement in the United Kingdom. He began his long career as a writer at the end of the 18th century, at which time he published the translation of the ballads of G.A. Bürger, The Chase, and William and Helen (1796). Among his most acclaimed writings, are The Lady of the Lake (1810), Guy Mannering (1815), Rob Roy (1817), Ivanhoe (1819), The Monastery (1820), and The Talisman (1825). Most of these works were published anonymously. However, towards the end of the 1820s, the identity of the author was revealed.
Early years
Son of Walter Scott, lawyer, and Anne Rutherford, with only two years of age, contracted polio. Disease that seriously affected his health, leaving as a limp in his right leg. At this time, he lived with his grandfather Robert Scott in Sandyknowe. After four years he returned to Edinburgh, city in which he carried out his studies. Subsequently entered the University of Edinburgh, where he studied law, as did his father.
After graduating he began to practice his profession. At this time, he began to collect information about the myths and legends of Scotland while carrying out his duties. This theme was addressed by Scott in different works.
Literary career
Towards the end of the 1790s he began his career, translating the work of Gottfried A. Bürger, Leonore, as well as the ballads included in The Chase, and William and Helen (1796). Shortly thereafter translated Götz von Berlichingen of Goethe, book based on the life of the poet and adventurer Götz von Berlichingen, known as Iron Hand. At the beginning of the 19th century, he published the collection of ballads collected during his travels, entitled Minstrels of the Scottish Border (1802). This includes famous Scottish ballads such as The Young Tamlane, The Twa Corbies, The Douglas Tragedy, The Wife of Usher’s Well, The Cruel Sister and The Daemon Lover. After its publication, the work had little reception, however, the author continued to update this collection until 1830.
In the mid-1800s, he published the poem The Lay of the Last Minstrel (1805), a writing that was well-received, followed by Ballads and Lyrical Pieces (1806), a written work while serving as secretary of the courts of justice in Edinburgh. Later, Scott published Marmion: a Tale of Flodden Field (1808), a romantic historical poem that ends with the death of the protagonist in the Battle of Flodden Field. Two years later, he published The Lady of The Lake (1810), one of his most acclaimed poems by the author.
He later published The Vision of Don Roderick (1811) and The Bridal of Triermain (1813). In 1814 he published his first novel Waverley, a work set in the Jacobite uprising of 1745 in the United Kingdom; it was published anonymously since the author was a public official. After its publication, the work became a success.
Since then, he published several novels using different pseudonyms as Author of Waverley, Jebediah Cleisbotham, Crystal Croftangry, and Lawrence Templeton, among others. It should be noted that at this time the author’s identity was a fairly well-known secret. After Waverley (1814) wrote Guy Mannering (1815), The Antiquarian (1816), Rob Roy (1818) and Ivanhoe (1819), a novel story set in medieval England that tells the story of Wilfredo de Ivanhoe, noble Saxon, likewise, delves into the contradictions between the Saxon people and the Normans. This is one of the most outstanding works of the author.
Three years later he published The Adventures of Nigel (1822) and Peveril of the Peak (1822), followed by Quintin Durward (1823), a novel set in France by Louis XI. Later published Redgauntlet (1824), Tales of the Crusaders (1825) and Woodstock or The Knights: A Story of 1651 (1826).
That same year the author’s identity was revealed; year in which the author went through one of the most difficult moments of his life, given that his wife Charlotte Carpenter died and the Constable publishing house, in which he had invested a large amount of money he went bankrupt. Leaving a debt of 130,000 pounds, which he paid for the rest of his life.
At the end of the 1820s, he published The Life of Napoleon Buonaparte (1827), a book in which he delves into the life of Napoleon Bonaparte. The following year he published The Beautiful Young Woman of Perth (1828) and Tales of the Grandfather (1828), followed by History of Scotland (1829-1830), The Daughter of the Mist (1829), Bonnie Dundee (1830) and Letters on Demonology and Witchcraft (1831), the author’s last work. At this time, Scott, stopped writing and his health began to deteriorate rapidly. Scott passed away on September 21, 1832, was buried in Dryburgh Abbey.
The author’s work is considered a pioneer in the field of the historical novel, his writings are exalted by critics, since in these he realistically addresses historical events linked to his native Scotland and the Middle Ages, vividly evoking the context in which the protagonist of the history. Scott profoundly influenced the work of European writers, as well as painters and musicians; the writings of this have been represented in the theater, cinema, and television on several occasions.
Author
Marie Kondo
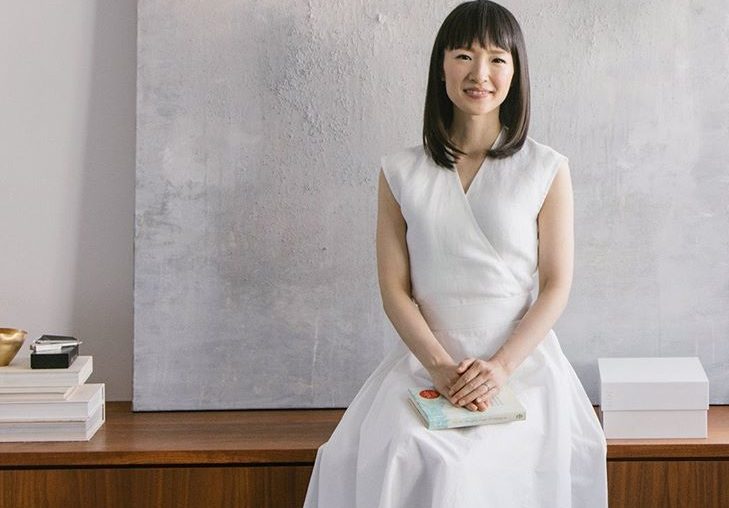

Marie Kondo Biography
Marie Kondo (October 9, 1984) was born in Tokyo, Japan. Writer and businesswoman, famous for being the creator of the Konmari method. A system that explains the proper way of organizing the home so that only the necessary is available and what makes the owner happy, avoiding the accumulation derived from the tendency to cling to the past. Kondo’s method has become a trend, after the publication of her first book The Magic of Order (2011), in which she delves into the method and highlights the positive aspects of order, emphasizing the serenity and relaxation an organized house inspires, which will be reflected in the daily life of people living in the home.
Early years
Kondo was interested at an early age in order and cleanliness, influenced by magazines about decoration and the home that her mother bought. While growing up, she spent a lot of time alone, since her mother took care of her younger sister, who at that time was just a baby. During these years she studied and continued to cultivate her love for order. When she entered the institute she began ordering the shelves while other students practiced sports.
Upon entering the University of Tokyo, she noticed that ordering helped her stay calmed and release the stress produced by the studies and partials. One day she organized for the first time she experienced a state of total calm and perfect order, which motivated her to choose the organization as a profession.
The Konmari method
At 19, while studying at the University of Tokyo, she became a consultant and created the Konmari method, a System in which she explains the proper way to organize the home and other spaces, so that they become spaces of inspiration and serenity, which to some extent influences the mental health of the people who inhabit the place. The Kondo method proposes the elimination of unnecessary things, likewise, on a more personal level, it promotes the termination of unproductive relationships that do not positively influence the person. The goal of the system is to bring happiness and serenity to the person who carries it out.
Konmari is based on the steps that Kondo followed in the organization of her home, as well as certain aspects of Eastern philosophy, feng shui, and inspirational coaching. This is divided into five steps: the first is the selection and organization of clothing, only what is used is chosen, looks good or produces happiness to the owner. After the selection must be organized so that everything is visible and accessible.
The second is focused on books, only those that are of great importance are chose, preventing them from exceeding 30 books. The next step is the papers, keeping what is in force or necessary, then they are stored in folios. The fourth step is the komono, also understood as various objects that you have in the home such as photos, CDs, magazines, among others, of these should only remain what has great emotional value.
Finally, sentimental articles should be selected and organized, as mentioned above, only objects that have a deep sentimental value and that produce happiness should be chosen. If that is not the case, it should be discarded since only objects that do not contribute to growth would be accumulating and peace of the person. This method has been widely disseminated since the publication of Kondo’s first book, entitled The Magic of Order (2011), which was well-received by the public. Shortly thereafter launched happiness after order (2012), in which delves into the method and well-being that it brings; subsequently published The magic of order. An illustrated novel (2017).
These books were transformed into lectures, audiobooks, and articles, through which, Kondo, has become one of the most prominent figures of recent years. After the publication of these, the author has participated in various radio and television programs in Japan and other countries, such as Ellen Show and Rachael Ray Show. Also has been interviewed by the Time Magazine, The New York Times, The Wall Street Journal, Vogue Magazine, among others.
In 2015, she was included in the list of the 100 most influential people in the world created by Time magazine, list in which the outstanding Japanese writer Haruki Murakami has also been included. At present, her company has a long list of clients whom she helps transform her spaces into places of inspiration and serenity. In January 2019, the series Tidying Up with Marie Kondo was launched from Netflix, in which Kondo is seen visiting and organizing homes based on her method.
Author
Joël Dicker

Joël Dicker Biography
Joël Dicker (June 16, 1985) Born in Geneva, Switzerland. Swiss writer considered one of the most relevant writers of recent years. Before devoting himself fully to writing he studied for a short time Drama in Paris, and Law at the University of Geneva, a career that ended in 2010; Dicker rose to fame that same year, winning the prestigious Prix des Ecrivains Genevois award, an award aimed at highlighting unpublished works. Subsequently published the successful books: The Last Days of Our Fathers (2011), The Truth About The Harry Case Quebert (2012), The Book Of The Baltimore (2015) and The Disappearance Of Stephanie Mailer (2018). Their success turned Dicker into a phenomenon of international sales.
Early years
Son of a high school teacher and a bookstore; he has three brothers. Dicker spent his childhood in Geneva, the city where he began his academic training. While studying he began to be interested in writing, an interest he cultivated by becoming the manager of nature and animal magazine. After attending elementary school, he entered the Collège Madame de Staël, an institution where he continued polishing his writing skills. It is worth mentioning that although he was attracted to writing, he did not like to study.
At the end of this training period, he moved to Paris, where he began taking acting classes at the renowned French drama school, Cours Florent. After a year he dropped out of school and returned to his hometown, where shortly thereafter he began studying law at the University of Geneva. At 19 he wrote his first work, The Tiger (2005), a short story set in Tsarist Russia, specifically in the government of Tsar Nicholas II. Five years later he graduated, obtaining the title of Lawyer.
Joël Dicker’s work
The trajectory of the young writer began in the mid-2000s, at which time he published the story, The Tiger (2005), a work he presented in a youth literary contest but was dismissed since for the judges it was suspected that such work was written by someone so young. In the story, he deepens on topics such as existential dilemmas, violence, the possibility of redemption and the great questions that human beings pose, this was set in the government of the last Tsar of Russia, Nicholas II.
Five years later he won the Prix des Ecrivains Genevois prize, awarded by the Geneva Writers Society for the best manuscript not published for the work The Last Days of Our Fathers, written that was published a year later thanks to the prize. The Last Days of Our Fathers (2011), set in the period covered by World War II, focused on the strategy of Winston Churchill and the actions of the Special Operations Executive, an espionage agency infiltrated in the Nazi army lines.
In 2012, he published the criminal mystery, The Truth About The Case Harry Quebert (2012), a work that revolves around Marcus Goldman’s investigation of the murder of Nola Kellergan, who was close to the friend and mentor of writer Harry Quebert. This paper was awarded the Goncourt Prize and the Novel Grand Prix of the French Academy.
In 2018, the work was adapted to television in the miniseries format, which was directed by Jean-Jacques Annaud and starring Patrick Dempsey. Three years after the publication of The Truth About The Harry Quebert Case (2012), The Baltimore Book (2015) came out, written that continues the investigations of the young writer Marcus Goldman, this time he investigates the Goldman family of Baltimore, from the period of opulence to the decline of the family and the emergence of drama.
The most recent work of the author is The Disappearance of Stephanie Mailer (2018), a thriller that revolves around the mysterious disappearance of a journalist who at that time had discovered the irregularities of an old homicide case, by revealing this information to the police officer in charge of case disappears.
Author
Henri de Saint-Simon

Henri de Saint-Simon Biography
Claude Henri de Rouvroy, Count of Saint-Simon (October 17, 1760 – May 19, 1825) was born in Paris, France. Historian and political theorist, he was one of the founders and theorists of modern socialism. The Count of Saint-Simon was part of the military who fought in the War of Independence of the United States (1775-1783), later joined the revolutionary cause in Paris becoming a Republican.
He was appointed president of the Paris Commune in 1792, at which time he renounced his noble title and changed his name to Claude Henri Bonhomme, after being accused of speculation and spending a short time in jail focused on writing, publishing the books The industrial system (Du système industriel) and New Christianity (Nouveau Christianisme).
Early years
He was born into an aristocratic family. Among his relatives is Duke Louis de Rouvroy de Saint-Simon, author of Memories (1739-1752), a book in which he described the court of Louis XIV of France. Due to family tradition, he began his military career at an early age actively participating in the United States War of Independence (1775-1783), in favor of the colonies. After returning to the country began the revolutionary movement that ended in the outbreak of the French Revolution (1789-1799), political and social conflict that marked the history of the eighteenth century, driving profound changes in various parts of the world as the establishment of the republican model. During the development of the revolution, Saint-Simon became a Republican and was appointed president of the Paris Commune in 1792.
In the course of his government he was accused of speculation of national assets and criticized for his close relationship with Georges-Jacques Danton, which caused him to be detained between 1793 and 1794. During the Directory (1795-1799), Saint-Simon lived on comfortably, since he had a good fortune, at that time his home was visited by prominent figures of the time such as Gaspard Monge, Joseph-Louis de Lagrange, and Guillaume Dupuytren. Later, he traveled to Germany, the United Kingdom, and Switzerland, in the course of the trip he began writing his first works.
Literary Works
At the beginning of the 19th century, he published his first work entitled Letter from a resident in Geneva to his contemporaries (Lettres d’un habitant de Genève à ses contemporains), where he outlined what he would later define as capacity theory. After spending several years living comfortably, his fortune began to decrease, which is why he faced serious economic problems. To sustain himself he wrote several scientific and philosophical articles with which he managed to stabilize his economic situation. For this same period he mentioned one of his best-known phrases in the newspaper L’Organisateur:
If France lost its main physicists, chemists, bankers, merchants, farmers, blacksmiths, etc., it would be a body without a soul. On the other hand, if I lost all the men considered most important in the State, the fact would not bring more pain than the sentimental one
This statement was seen negatively and he was prosecuted for it. Starting the 1820s he published his next work called The Industrial System (Du système industriel, 1821) and four years later he published his most exalted work New Christianity (Nouveau Christianisme, 1825), a work in which he criticized the doctrine of Jesus and sat the basis for establishing a new Christianity that was more in line with the original evangelical teachings. After the publication of the book, he was ruined again, which is why he planned to take his life off of a shot. However, he failed and was injured in one eye, a short time later driven by one of his disciples decided to create the newspaper Le Producteur, but shortly before his appearance, he passed away. The renowned French theorist died on May 19, 1825, in Paris.
After his death, his approaches and ideas were disseminated by his disciples who created the ideological movement known as Saint-simonianism which was of great relevance in later generations influencing the formation of utopian socialism. His ideas were exalted by philosophers Karl Marx and Émile Durkheim. Saint-Simonianism’s thinking was based on his personal experience during the development of the French Revolution and the fall with the coup d’état orchestrated by Napoleon Bonaparte. In this, he stated that the government should be managed by industrialists such as workers, peasants, and owners, mentioned that the place that clerics had in the social order should be occupied by scientists; religion should guide social classes so that they improve their quality of life.
Finally, he mentioned that the redistribution of goods should be based on the capacity of each individual. These ideas influenced the work of Auguste Comte, John Stuart Mill, and various socialist philosophers.



















































